Monkeypox (Mpox), a virus similar to smallpox, has gained attention in recent years due to its increasing spread across the globe. Although it doesn’t spread as easily as smallpox, Monkeypox can still cause serious illness and discomfort. This article will break down what Monkeypox is, including its symptoms, how it spreads, and how you can prevent it.

What is Monkeypox?
It is possible for people to contract the infectious disease monkeypox from animals. It’s caused by the Monkeypox (Mpox) virus, which is part of the Orthopoxvirus family. The illness usually resolves on its own after a few weeks. While not as contagious as smallpox, Monkeypox can still be passed through close contact with someone or something infected.
Symptoms of Monkeypox
Monkeypox (Mpox) symptoms typically appear 2–14 days after coming into contact with the virus. Common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
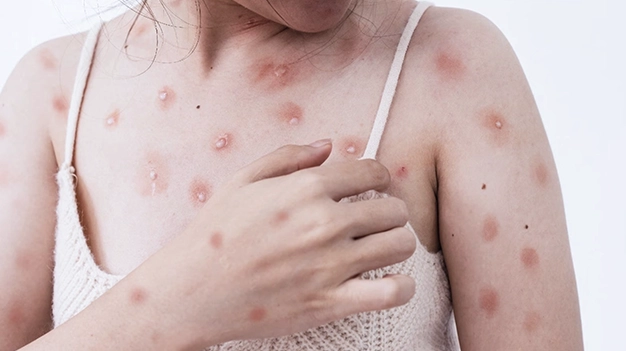
- Skin rash
The rash usually begins as small, red bumps that might resemble pimples or blisters. These bumps can appear on the face, hands, feet, chest, abdomen, and even the genitals. Over time, the bumps may develop into pustules and scabs before eventually healing.
How Monkeypox Spreads
Monkeypox can be spread through close contact with an infected person or animal. It spreads in several ways:
- Getting close to an infected person’s rash or scabs
- Coming into contact with bodily fluids
- Handling contaminated items like bedding or clothing
Although less common, the virus can also spread through respiratory droplets.
Preventing Monkeypox
There is no vaccine specifically for Monkeypox (Mpox) at the moment, but the smallpox vaccine is highly effective at preventing it. Unfortunately, this vaccine is not widely available.
Take these precautions to keep yourself safe:
- Keep your distance from sick folks.
- Make frequent use of soap and water to wash your hands.
- Stay away from wild animals or their meat.
- Practice safe sex.
Treating Monkeypox

There isn’t a specific treatment for Monkeypox (Mpox). The illness usually clears up on its own, and symptoms can be managed with over-the-counter medications. Hospitalization might be necessary in more serious cases, though.
Why Monkeypox is a Global Health Issue
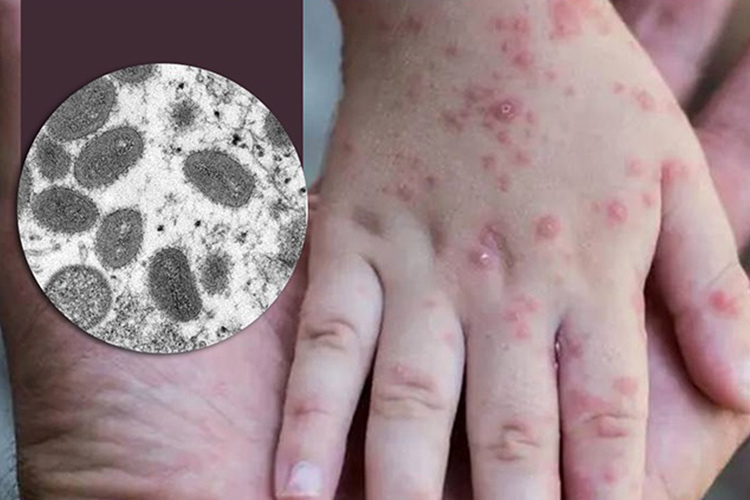
Monkeypox has become a global health concern due to its growing prevalence in various parts of the world, including Africa, Europe, and the Americas. India reported its first Monkeypox cases in 2022, though the number of cases has remained lower compared to other countries. The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared Monkeypox a public health emergency of international concern.
As cases continue to rise, staying informed about Monkeypox (Mpox) is crucial. By understanding its symptoms, how it spreads, and how to prevent it, we can better protect ourselves and those around us.
Top 5 Hospitals for Treatment in Delhi NCR, INDIA
- Max Hospital
- Forties Hospital
- Medanta Hospital
- Artemis Hospital
- Shalby Sanar International Hospitals
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of Monkeypox?
- Fever, headache, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, and a rash are typical symptoms of Monkeypox.
How does Monkeypox spread?
- Monkeypox spreads through close contact with an infected person’s rash, bodily fluids, or contaminated materials.
Is there a specific vaccine for Monkeypox?
- There is no specific vaccine for Monkeypox, but the smallpox vaccine can help prevent it.